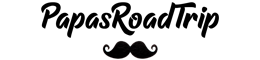When it comes to upgrading your car’s exhaust system, you might have stumbled upon two terms that often get mixed up: test pipe and downpipe. But which one is right for your ride?
Understanding the difference between a test pipe and a downpipe can unlock better performance, sound, and even fuel efficiency. If you’re looking to boost horsepower or just want to know what’s under your car’s hood, this guide will clear the confusion and help you make the best choice.
Ready to find out how these parts impact your driving experience? Let’s dive into the key differences between test pipes and downpipes so you can take your vehicle to the next level.
Exhaust System Basics
The exhaust system is a key part of any vehicle’s engine setup. It directs harmful gases away from the engine and reduces noise. It also helps improve engine efficiency and power. Understanding its components helps in making better upgrades or repairs.
Two important parts often discussed are the downpipe and the test pipe. Each plays a different role in the exhaust system. Knowing their functions can guide you in choosing the right option for your car.
Function Of Downpipes
The downpipe connects the turbocharger or exhaust manifold to the rest of the exhaust system. It guides exhaust gases from the engine to the catalytic converter and beyond. This pipe usually includes sensors and heat shields. It helps control emissions and reduces engine noise. A well-designed downpipe improves exhaust flow and engine performance.
Role Of Test Pipes
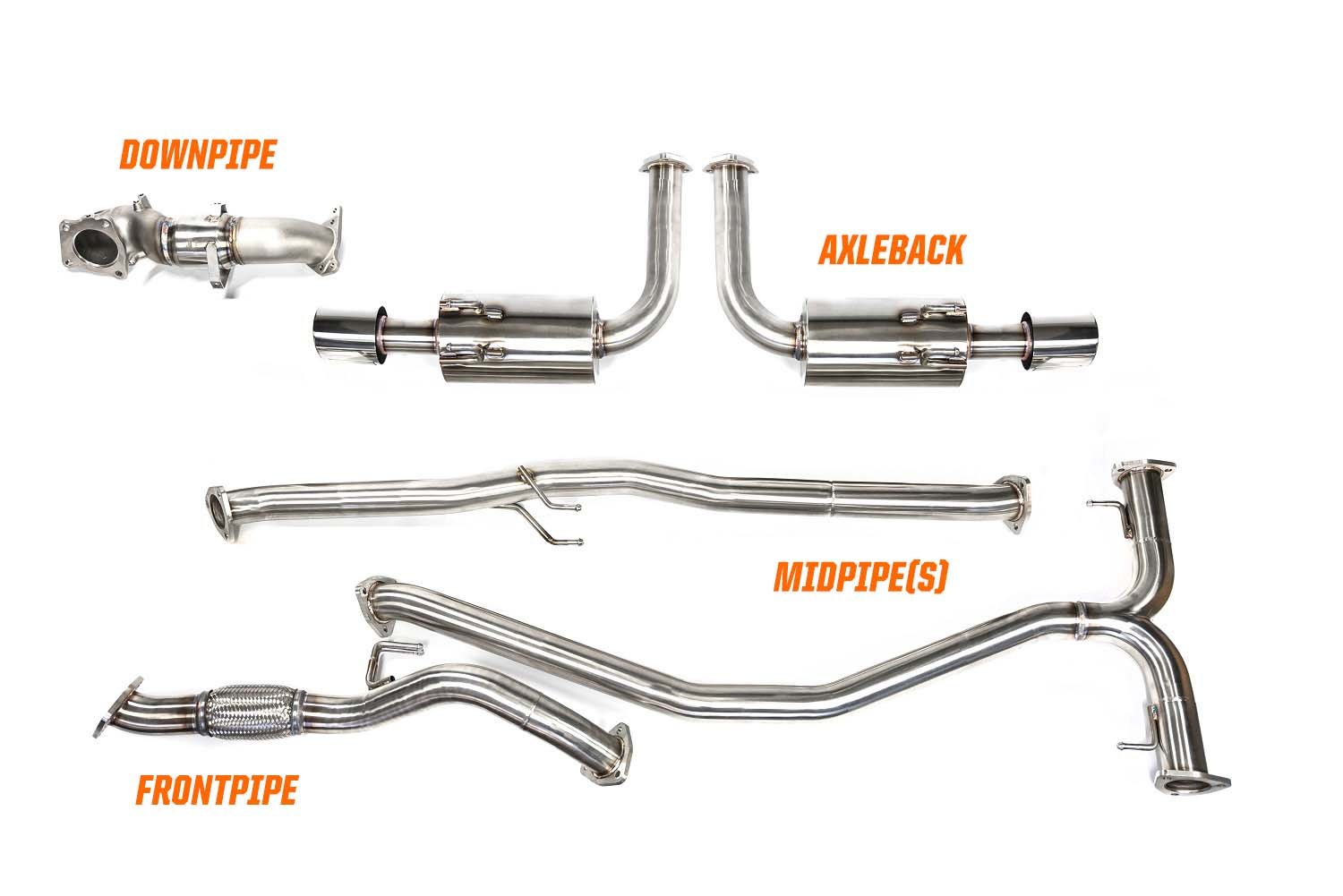
Test pipes replace the catalytic converter with a straight pipe. They allow exhaust gases to flow more freely. This reduces backpressure, which can increase horsepower and torque. Test pipes often make the exhaust sound louder and more aggressive. They are popular for off-road and racing uses. However, test pipes do not filter emissions and are illegal on public roads in many areas.
Credit: www.27won.com
Physical Differences
The physical differences between a test pipe and a downpipe affect their function and installation. These parts are key components of a car’s exhaust system. Understanding their build helps you choose the right upgrade for your vehicle.
Length And Complexity
A downpipe is usually longer than a test pipe. It connects the turbo or exhaust manifold to the rest of the exhaust system. Downpipes often have curves and bends to fit around other parts. This makes them more complex in shape and design.
Test pipes are shorter and simpler. They replace the catalytic converter with a straight pipe. This results in a direct path for exhaust gases. The simple design means fewer bends and less complexity overall.
Components Included
Downpipes include several components. They often house the catalytic converter or pre-catalytic converter. Heat shields and oxygen sensor ports are also part of downpipes. These additions help control emissions and protect nearby parts from heat.
Test pipes remove the catalytic converter entirely. They do not include heat shields or sensor mounts. This absence leads to a lighter and more open pipe. However, it also means test pipes do not reduce harmful emissions.
Performance Impact
Performance impact is a key factor in choosing between a test pipe and a downpipe. Each affects your car’s engine in unique ways. Understanding how these parts influence power, exhaust flow, and temperature helps you make a smart choice. Below, we explore their differences in key performance areas.
Horsepower And Torque Gains
Test pipes often boost horsepower and torque more than downpipes. They remove the catalytic converter, reducing restrictions in the exhaust system. This allows exhaust gases to escape faster. Faster gas flow improves engine breathing, leading to better power output. Downpipes can also improve power, but gains are usually smaller. They keep the catalytic converter, which adds some backpressure.
Exhaust Flow And Backpressure
Test pipes offer smoother exhaust flow by eliminating the catalytic converter. This reduces backpressure and helps the engine push out exhaust gases easily. Lower backpressure means the engine works more efficiently. Downpipes maintain some backpressure due to the catalytic converter’s presence. This can slightly limit exhaust flow but helps reduce emissions. The choice depends on whether you want maximum flow or cleaner exhaust.
Effect On Exhaust Temperatures
Test pipes generally lower exhaust temperatures. Without the catalytic converter, exhaust gases stay hotter longer but exit faster. This can reduce heat buildup near the engine. Downpipes keep the catalytic converter, which absorbs some heat. This may cause higher temperatures around the exhaust system. Cooler exhaust temps help protect engine parts and improve longevity. Consider your driving style and climate when choosing.

Credit: www.roadraceengineering.com
Sound And Weight
The sound and weight of your vehicle’s exhaust system greatly affect driving experience and performance. Test pipes and downpipes differ in these aspects, impacting noise levels and overall vehicle weight. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right option for your car.
Changes In Exhaust Tone
Test pipes remove the catalytic converter, creating a louder and more aggressive exhaust sound. This happens because exhaust gases flow freely without restriction. The tone becomes deeper and more raw, appealing to those who want a sportier sound.
Downpipes keep the catalytic converter or include high-flow cats, so the sound remains quieter. The exhaust tone is smoother and less harsh. It offers a balance between performance and noise control, suitable for street use.
Weight Reduction Benefits
Test pipes are simpler and lighter than downpipes. Removing the catalytic converter reduces the overall weight of the exhaust system. This helps improve vehicle acceleration and handling by lowering the car’s mass.
Downpipes are heavier due to added components like catalytic converters and sensors. They add weight but maintain emission standards. Weight difference may be small but noticeable for performance enthusiasts.
Legal And Emissions Considerations
Understanding the legal and emissions aspects of exhaust modifications is crucial. Test pipes and downpipes affect vehicle emissions differently. These differences impact road legality and compliance with regulations. This section explores these important factors.
Emission Control And Catalytic Converters
Catalytic converters reduce harmful gases in exhaust emissions. They convert pollutants into less harmful substances. Downpipes usually include or connect to catalytic converters. Test pipes replace catalytic converters with straight tubing. Removing converters increases emissions of carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. This harms air quality and violates environmental laws.
Legality Of Test Pipes
Test pipes are often illegal for street use. They bypass emission control devices required by law. Many states and countries ban vehicles without catalytic converters. Using test pipes can lead to fines and failed inspections. Some sellers label test pipes as “off-road use only” to avoid legal issues. Installing test pipes on public roads risks penalties and voids warranties.
Inspection And Compliance Issues
Vehicles with test pipes usually fail emissions inspections. Inspectors check for catalytic converters and emission controls. Missing converters cause automatic failure in many regions. Downpipes with catalytic converters help vehicles pass inspections. Compliance with local laws ensures legal driving and reduces pollution. Drivers should verify regulations before modifying exhaust systems.
Cost And Application
Understanding the cost and application of test pipes versus downpipes helps choose the right exhaust part. Both affect vehicle performance and emissions differently. Their prices and best uses vary based on material and design.
Price Differences
Test pipes usually cost less than downpipes. They are simpler tubes without catalytic converters. Downpipes include cats and sensors, making them more complex and expensive. Installation costs also differ due to complexity. Test pipes can save money upfront but might cause legal issues. Downpipes are pricier but often street-legal and compliant with regulations.
Best Use Cases For Each
Test pipes fit well in race or off-road vehicles. They improve exhaust flow by removing emissions parts. This boosts horsepower but increases pollution. Downpipes work best for street-driven cars. They balance power gains and emissions control. Downpipes suit daily drivers requiring legal compliance. Test pipes are ideal for track days or tuning projects where emissions rules are less strict.
Choosing Between Test Pipe And Downpipe
Choosing between a test pipe and a downpipe affects your vehicle’s exhaust system and overall driving experience. Both parts influence engine performance and sound but serve different purposes. Understanding these differences helps you pick the right upgrade for your needs.
Performance Vs. Noise Trade-offs
A downpipe usually includes a catalytic converter. It balances performance and emissions control well. This keeps your car street-legal and reduces harmful gases.
Test pipes remove the catalytic converter. This boosts exhaust flow and horsepower. The engine breathes easier and performs better at high speeds. But test pipes increase noise levels significantly. The sound becomes louder and more aggressive.
Choosing a test pipe means accepting louder noise and possible emissions issues. A downpipe offers improved power but keeps your car quieter and cleaner.
Street Use Vs. Race Use
Downpipes fit street cars better. They maintain legal emissions and pass inspections. This makes them a safer choice for daily driving.
Test pipes suit race cars or off-road vehicles. They maximize power by removing restrictions. The louder sound is less of an issue in racing environments.
Using a test pipe on the street may cause legal problems. It can fail emissions tests and produce more pollution. Downpipes provide a good middle ground for street and occasional track use.
Credit: chanakyamandal.org
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Test Pipe And Downpipe The Same?
A downpipe connects the turbo to the rest of the exhaust and includes a catalytic converter. A test pipe replaces the catalytic converter with a straight pipe, improving flow but is often illegal.
Why Are Test Pipes Illegal?
Test pipes are illegal because they remove catalytic converters, which control harmful vehicle emissions. This violates environmental laws and increases pollution.
What Are The Pros And Cons Of Test Pipes?
Test pipes boost horsepower and reduce weight by removing catalytic converters. They improve exhaust flow but increase emissions and often are illegal.
How Much Hp Do Test Pipes Add?
Test pipes typically add 5 to 15 horsepower by reducing exhaust backpressure and improving gas flow efficiency.
What Is The Main Difference Between Test Pipe And Downpipe?
A downpipe includes a catalytic converter; a test pipe replaces it with a straight pipe.
Conclusion
Choosing between a test pipe and a downpipe depends on your needs. Test pipes offer simpler design and better flow but remove emissions controls. Downpipes include catalytic converters and meet legal standards. Each affects engine performance and sound differently. Understanding these differences helps you decide what suits your vehicle best.
Keep in mind local laws before making changes. Proper choice leads to better exhaust flow and driving experience.