Car overheating can be a puzzling issue. Especially when the coolant is full.
Why does this happen? Many drivers face the frustrating problem of their car overheating despite a full coolant reservoir. This can be alarming and inconvenient. Overheating can damage your engine and lead to expensive repairs. Understanding the reasons behind this issue is crucial.
It helps in taking timely actions and preventing further damage. In this blog, we will explore the common causes of a car overheating even with sufficient coolant. We will also discuss possible solutions to keep your vehicle running smoothly. Whether you’re a seasoned driver or a newbie, this information will be valuable for you. Stay tuned to learn more about maintaining your car’s cooling system effectively.
Common Reasons For Car Overheating
Experiencing car overheating with full coolant can be baffling. Understanding the common reasons for this issue is key to preventing engine damage. Several factors can cause a car to overheat, even when the coolant level is adequate. Below are some common reasons your car might be overheating.
The thermostat regulates the engine’s temperature. It controls the flow of coolant to the radiator. A stuck thermostat can block coolant flow. This prevents the engine from cooling down. As a result, the engine overheats.
The radiator cools the engine by dissipating heat. If it’s clogged or damaged, it can’t perform well. This leads to overheating. Sometimes, the radiator fan might also fail. This reduces airflow and cooling efficiency.
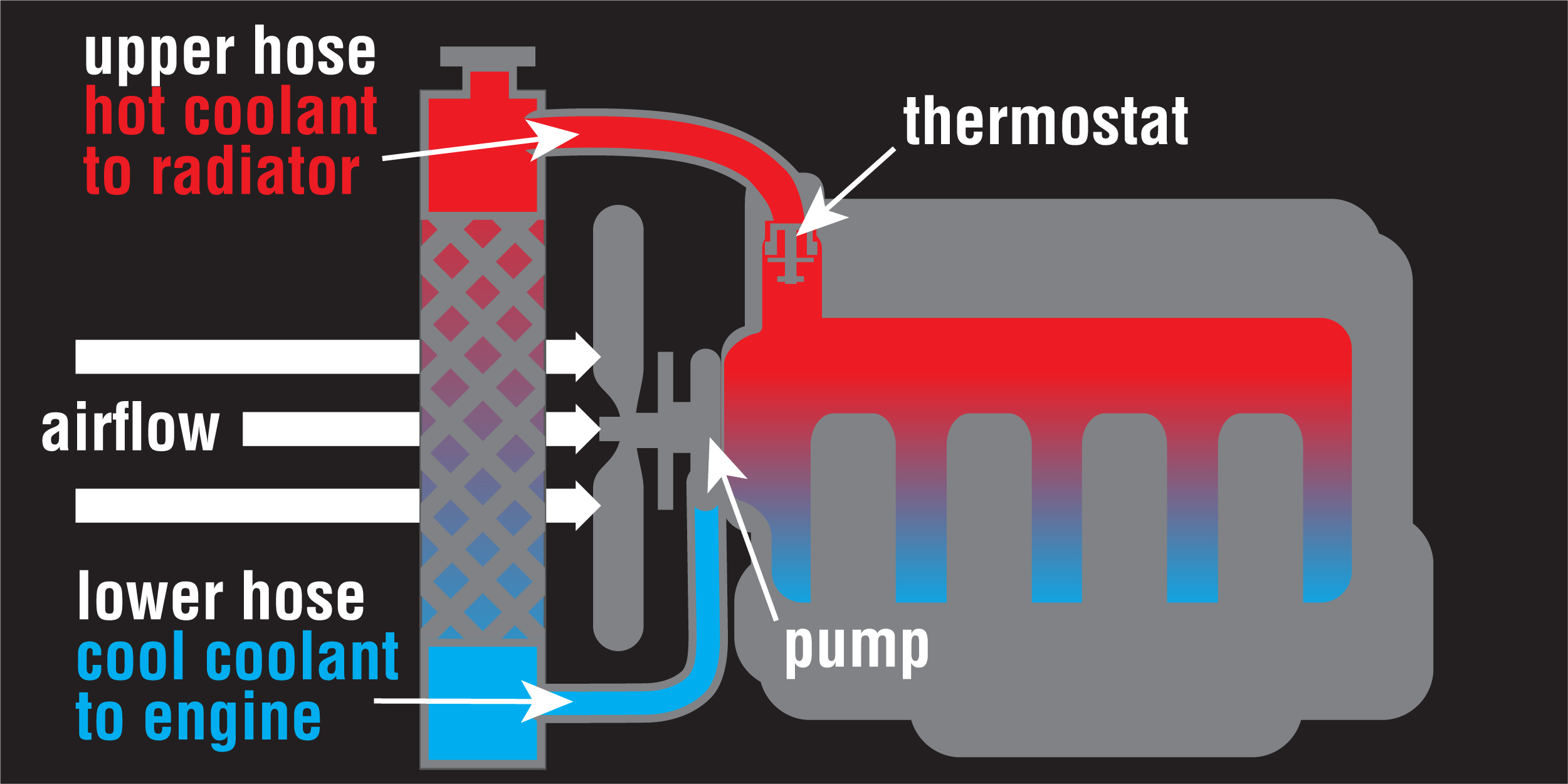
Credit: bgfindashop.com
Faulty Thermostat
A faulty thermostat can cause your car to overheat, even with full coolant. The thermostat regulates the engine temperature by controlling coolant flow. If it fails, it can lead to serious engine issues.
Symptoms
One common symptom is the engine overheating quickly. The temperature gauge might spike rapidly. You might also notice inconsistent temperature readings. Another sign is poor heater performance. If your car heater blows cold air, it could be due to a faulty thermostat.
Repair Options
Repairing a faulty thermostat usually involves replacing it. First, locate the thermostat in your car. It is often near the radiator. Consult your car’s manual for exact details. You may need basic tools like a wrench and screwdriver. Drain the coolant before removing the old thermostat. Install the new thermostat and refill the coolant. Check for any leaks and monitor the temperature gauge. If unsure, consider consulting a professional mechanic.
Radiator Issues
Radiator issues are common causes of car overheating, even with full coolant. The radiator plays a key role in cooling the engine. If it fails, the engine can overheat quickly. Below are some common radiator problems that can lead to overheating.
Clogged Radiator
A clogged radiator restricts the flow of coolant. This blockage prevents heat from dissipating. Over time, debris and dirt can build up inside. This buildup reduces the radiator’s efficiency. As a result, the engine may overheat.
Regular maintenance can help prevent clogs. Flushing the radiator removes accumulated debris. This simple step can keep your radiator working well.
Leaking Radiator
A leaking radiator loses coolant. This loss reduces the coolant level in the system. With less coolant, the engine cannot cool properly. Small leaks can be hard to detect. Over time, they can lead to significant coolant loss.
Check for signs of leakage around the radiator. Wet spots or puddles under the car may indicate a leak. Repairing leaks promptly can prevent overheating issues.
Water Pump Problems
Experiencing car overheating despite having full coolant? The water pump may be the issue. The water pump plays a crucial role in keeping your engine cool. It circulates coolant through the engine. When it fails, your engine can overheat rapidly. Understanding the symptoms and replacement process can help you address this issue.
Symptoms Of Failure
Recognizing water pump failure symptoms is vital. Here are the common signs:
- Engine Overheating: The most obvious sign. The coolant isn’t circulating properly.
- Coolant Leaks: Check under your car for puddles. Leaking coolant indicates a faulty pump.
- Whining Noise: A high-pitched noise from the front of the motor. This may signal a worn bearing.
- Steam from Radiator: Steam indicates your engine is too hot. The water pump may not be working.
- Corroded Pump: Visible rust or corrosion on the pump. This can hinder its performance.
Replacement Process
Replacing a water pump involves several steps. It’s often best to let a professional handle it. Here’s an overview:
- Disconnect the Battery: Safety first. Always disconnect the battery before starting.
- Drain the Coolant: Remove the radiator cap and drain the coolant into a container.
- Remove the Belt: Release tension and remove the serpentine belt.
- Access the Pump: Remove any components blocking access, such as the fan or radiator.
- Remove the Pump: Unbolt and remove the old water pump. Clean the mounting surface.
- Install the New Pump: Place the new pump and secure it with bolts. Ensure it’s tight and aligned.
- Reassemble: Reinstall any removed parts. Reattach the belt and refill the coolant.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the battery and start the engine. Check for leaks and proper operation.
Cooling Fan Malfunctions
Car overheating with full coolant can be puzzling. One common cause is a malfunctioning cooling fan. The cooling fan helps keep your engine at the right temperature. When it fails, the engine can overheat, even if the coolant levels are adequate.
Types Of Cooling Fans
There are two main types of cooling fans: mechanical and electric.
- Mechanical Fans: These fans are driven by the engine’s crankshaft. They are usually attached directly to the water pump pulley. Mechanical fans often have a fan clutch that engages or disengages based on the engine temperature.
- Electric Fans: These fans are powered by the car’s electrical system. They can be controlled by a thermostat or the engine control unit (ECU). Electric fans are more common in modern vehicles. They offer more precise control over cooling.
Troubleshooting Steps
If you suspect a cooling fan malfunction, follow these steps:
- Check the Fuse: A blown fuse can stop the fan. Locate the fuse box and inspect the fuse for the cooling fan. Replace it if necessary.
- Inspect the Relay: The relay controls the electric fan. A faulty relay can cause the fan to stop working. Test or replace the relay if needed.
- Test the Fan Motor: Use a multimeter to check if the fan motor is receiving power. If it is, but the fan doesn’t run, the motor may be faulty.
- Examine the Wiring: Look for damaged or disconnected wires. Reconnect or repair as needed.
- Check the Temperature Sensor: This sensor tells the fan when to turn on. If it fails, the fan may not activate. Replace the sensor if it is faulty.
Addressing cooling fan malfunctions can prevent engine overheating. Ensure your fan is in good working condition to maintain engine health.
Air Pockets In Cooling System
When your car overheats despite having full coolant, air pockets in the cooling system could be the culprit. These pockets prevent coolant from circulating properly, leading to overheating. Understanding the causes and solutions can help you avoid this issue.
Causes Of Air Pockets
Air pockets can form due to several reasons:
- Improper Coolant Refill: Failing to refill coolant correctly can trap air inside.
- Leaky Radiator Cap: A faulty cap can let air enter the system.
- Cooling System Leaks: Cracked hoses or a failing water pump can introduce air.
These factors disrupt the coolant flow and cause the engine to overheat.
Bleeding The Cooling System
Bleeding the cooling system removes air pockets. Follow these steps:
- Park on Level Ground: Ensure the car is on a flat surface.
- Cool Engine: Wait for the engine to cool completely.
- Open Radiator Cap: Slowly remove the cap to release any pressure.
- Start Engine: Run the engine and set the heater to the highest setting.
- Add Coolant: Pour coolant into the radiator until it reaches the top.
- Close Radiator Cap: Secure the cap and let the engine run for 15 minutes.
- Check Coolant Level: Turn off the engine and check the coolant level again.
This process ensures air is removed and coolant circulates properly.
Ensuring air pockets are eliminated can help maintain your engine’s health and prevent overheating.
Coolant Quality And Mixture
Coolant quality and mixture play a vital role in preventing car overheating. Even with a full coolant tank, poor quality or incorrect mixture can lead to engine problems. Understanding the importance of proper coolant mixture and identifying contaminated coolant can help maintain your car’s optimal performance.
Importance Of Proper Mixture
The correct coolant mixture keeps your engine running smoothly. A balanced mix of antifreeze and water is essential. An improper mixture can affect the coolant’s efficiency. It can either freeze in cold weather or boil in hot conditions. Both scenarios can cause your engine to overheat. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommended ratio to ensure the best results.
Identifying Contaminated Coolant
Contaminated coolant can harm your engine. Look for signs like discoloration or debris in the coolant. A rusty or oily appearance indicates contamination. A bad smell is another warning sign. Contaminated coolant loses its effectiveness. It can lead to overheating and engine damage. Regular checks can help you spot these issues early. Replace contaminated coolant to keep your engine safe.

Credit: carfromjapan.com
Engine Blockage
Experiencing car overheating with full coolant can be frustrating. The problem often lies in engine blockage. Blockages restrict the flow of coolant. As a result, the engine overheats. Understanding common blockage points can help. Clearing blockages can solve the issue.
Common Blockage Points
Several areas can block the coolant flow. The radiator is a prime suspect. Debris and rust can clog it. Thermostats can also fail. This prevents coolant from circulating. Hoses can become kinked or damaged. Water pumps may wear out. This reduces coolant movement. Heater cores can get blocked too.
Clearing Blockages
Clearing blockages is essential. Start with the radiator. Use a radiator flush to clean it. Replace a faulty thermostat. Check hoses for kinks or damage. Replace if necessary. Inspect the water pump. Ensure it works properly. Clean or replace a blocked heater core. Regular maintenance prevents future blockages.

Credit: www.automovill.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Is My Car Overheating With Full Coolant?
A faulty thermostat or water pump can cause overheating. Blocked radiator or coolant leaks can also be reasons.
Can A Bad Radiator Cap Cause Overheating?
Yes, a bad radiator cap can cause pressure loss. This leads to overheating.
How Do I Know If My Water Pump Is Bad?
Check for leaks, noise, or engine overheating. These signs indicate a bad water pump.
What Should I Check If My Car Overheats?
Check coolant level, radiator, thermostat, and water pump. Look for leaks or blockages.
Can A Clogged Radiator Cause Engine To Overheat?
Yes, a clogged radiator restricts coolant flow. This leads to engine overheating.
Conclusion
Keep your car’s cooling system in good shape to avoid overheating. Regular maintenance is crucial. Check for leaks, blockages, and faulty parts. A simple inspection can save you time and money. Don’t ignore warning signs. Addressing issues early prevents bigger problems later.
Stay safe on the road by keeping your engine cool. Trust a professional if needed. Proper care ensures a smooth and reliable drive.